Explore Our Main Services.

Heamatology
Hematology is the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. It involves the diagnosis and treatment of blood-related disorders like anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers.

Biochemistry / Clinical chemistry
Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes within living organisms, including the structure and function of biomolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It is essential to understanding the molecular basis of life and the mechanisms of disease.

Clinical pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids such as blood, urine, and tissue samples. It involves the use of various laboratory techniques to identify and quantify disease markers, pathogens, and other abnormalities in patient samples.
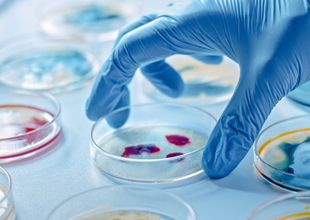
Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. It involves the study of their structure, function, and interactions with other organisms, and is essential to understanding disease, food production, biotechnology, and environmental science.

Histopathology / cytology
Histology and cytology are branches of biology that deal with the study of the structure, function, and composition of cells and tissues. Histology focuses on the study of tissues while cytology deals with the study of individual cells, their structure, function, and behavior.




